
 |
Exam-Style Questions on GraphsProblems on Graphs adapted from questions set in previous Mathematics exams. |
1. | GCSE Higher |
The equation of the line L1 is \(y = 2 - 5x\).
The equation of the line L2 is \(3y + 15x + 17 = 0\).
Show that these two lines are parallel.
2. | GCSE Higher |
René chooses two points at random on a sheet of graph paper by throwing two dice twice. He labels the points \(R\) and \(D\).
The scale used on both axes of the coordinate grid is 1 cm represents 1 unit.
\(R\) is the point \((5, 2)\) and \(D\) is the point \((1, 6)\).
(a) Calculate the length of the line segment \(RD\).
(b) Find the equation of the line that is perpendicular to \(RD\) and that passes through the point \((-5, 2)\).
Give your answer in the form \(y = mx + c\).
3. | GCSE Higher |
Which of the following lines is parallel to the x-axis?
\(y=-7\)
\(x-y=1\)
\(x=10\)
\(x+y=0\)
\(x=y\)
4. | GCSE Higher |
Show that line \(5y = 7x - 7\) is perpendicular to line \(7y = -5x + 55\).
5. | GCSE Higher |
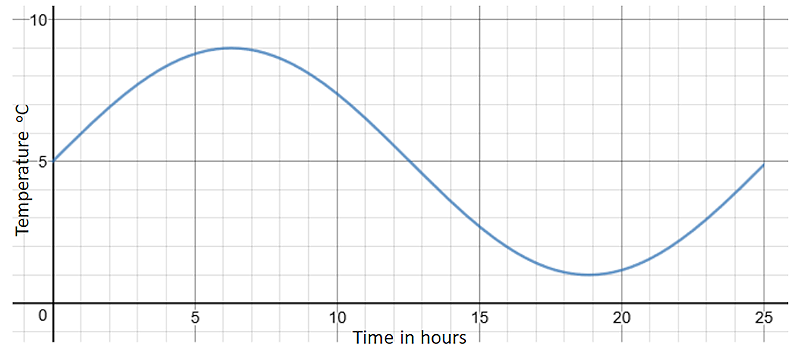
The graph shows the temperature recorded in a tent over a 25 hour period.
(a) For how many of the 25 hours is the temperature more than 5 degrees?
(b) By how much does the temperature change between hour 19 and hour 24?
6. | GCSE Higher |
The graph gives information about how the charging time in hours of an electric car relates to its range given as a distance in kilometres.
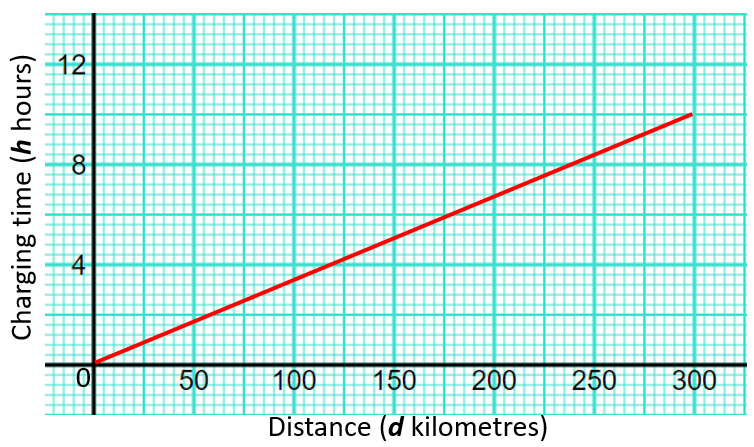
(a) Find the gradient of the graph.
(b) Interpret what the gradient of the graph represents.
7. | GCSE Higher |
A straight line goes through the points \((a, b)\) and \((c, d)\), where
$$a + 3 = c$$ $$b + 6 = d$$Find the gradient of the line.
8. | GCSE Higher |
Sketch the graph of \(y=0.5^x +1\) for \(0 \le x \le 5\) labeling the y intercept.
9. | GCSE Higher |
The straight line \(L\) has the equation \(4y = 3x + 5\).
The point A has coordinates \((6,7)\).
Find an equation of the straight line that is perpendicular to L and passes through A.
10. | GCSE Higher |
Lyana has drawn a time series graph to show the number of minutes she spent doing homework on some of the days in June 2021.
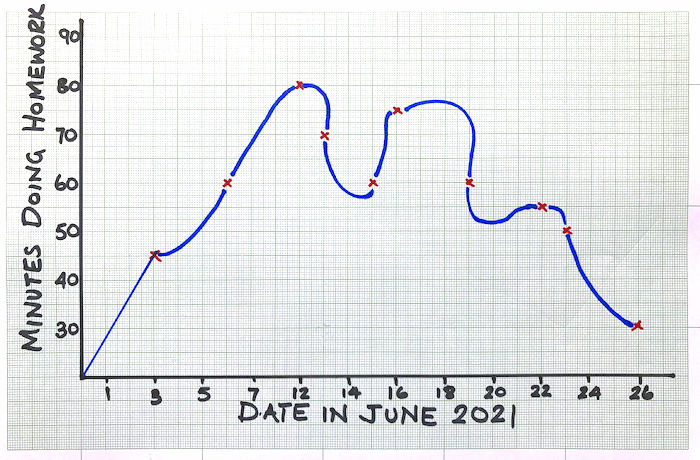
Write down two things that are wrong or could be misleading with this graph.
11. | GCSE Higher |
Write down the coordinates of the turning point on the graph of \(y = 9 - (x - 5)^2\)
12. | GCSE Higher |
(a) Use the red graphs to solve the simultaneous equations:
$$4x-7y=-47$$ $$3y=-5x$$(b) Use the blue graph to find estimates for the solutions of the quadratic equation:
$$x^2-5x+3=0$$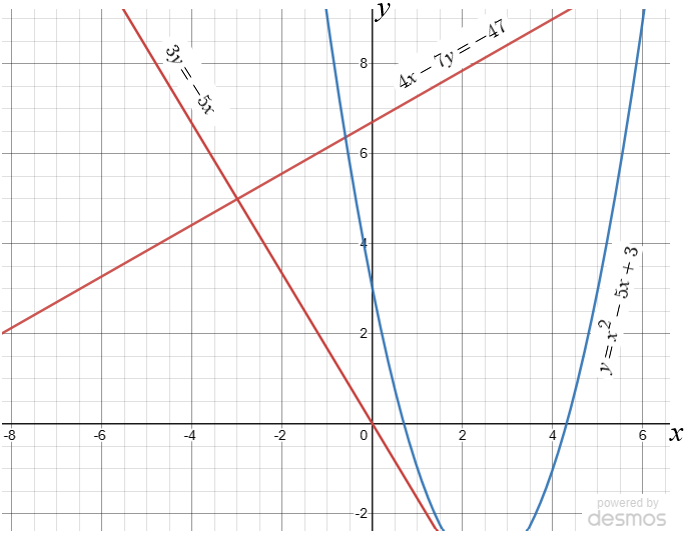
13. | GCSE Higher |
The graph shows the height of water in a container over a period time during which the water enters the container at a constant rate.
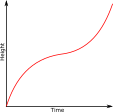
Which of the following might be a diagram of the container?
a. 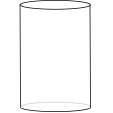 b.
b. 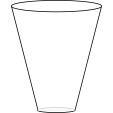 c.
c. 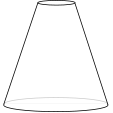 d.
d. 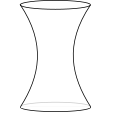 e.
e. 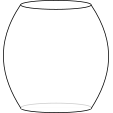
14. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram is of a container which is filled with water entering at a constant rate.

Which of the following might be the graph of height of the water in the container plotted against time?
a. 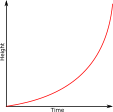 b.
b. 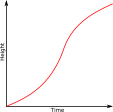 c.
c.  d.
d. 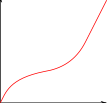 e.
e. 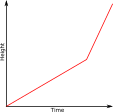
15. | GCSE Higher |
The images below show a graphic display calculator screen with different functions displayed as graphs.
a) Which function is trigonometric?
b) Which function is inversely proportional to \(x\)?
c) Which function is exponential?
d) Which function is proportional to \(x^3\)?
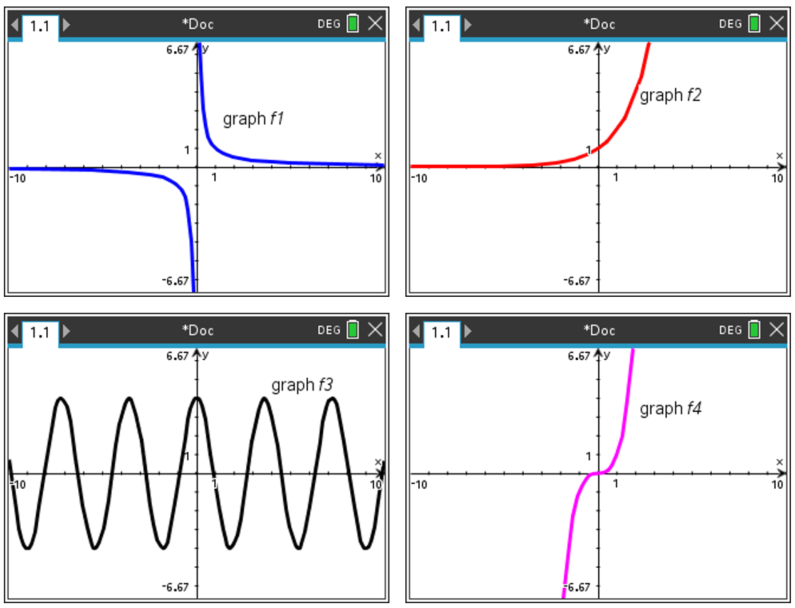
16. | GCSE Higher |
Match the equation with the letter of its graph
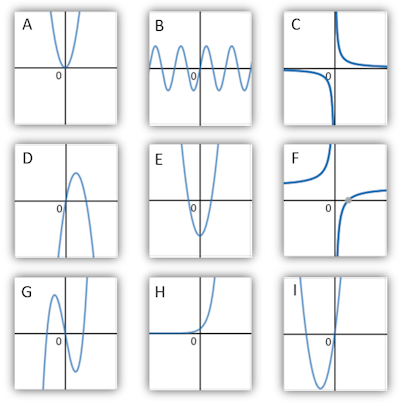
| Equation | Graph |
|---|---|
| $$y=3-\frac{10}{x}$$ | |
| $$y=2^x$$ | |
| $$y=\sin x$$ | |
| $$y=x^2+7x$$ | |
| $$y=x^2-8$$ | |
| $$y= \dfrac{5}{x} $$ |
17. | GCSE Higher |
(a) Complete the table of values for \(y=\frac{(x^3-5x)}{10}\)
| \(x\) | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| \(y\) | 0.2 | 1.2 |
(b) On the grid below, draw the graph of \(y=\frac{(x^3-5x)}{10}\) for values of \(x\) from -3 to 4.
18. | GCSE Higher |
A is the point (-5, -9) and B is the point (10, 1).
(a) Find the length of AB.
(b) Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
(c) C is a point on AB.
C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2.
Find the coordinates of C.
19. | GCSE Higher |
The graph of the curve A with equation \(y=f(x)\) is transformed to give the graph of the curve B with equation \(y=5-f(x)\).
The point on A with coordinates (3, 9) is mapped to the point W on B.
Find the coordinates of W.
20. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram shows part of the graph \(y=x^2-3x+6\).
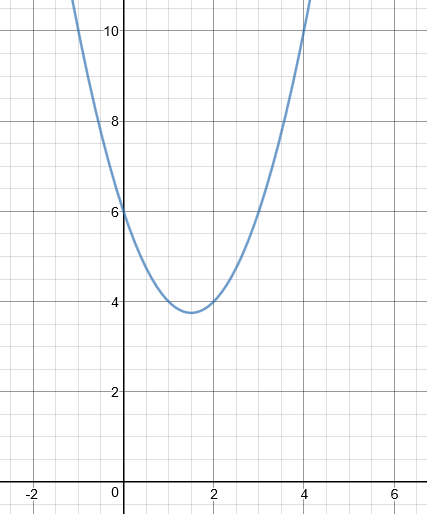
(a) By drawing a suitable straight line, use your graph to find estimates for the solutions of \(x^2 - 4x + 2 = 0\) to one decimal place.
(b) A is the point (2,4). Calculate an estimate for the gradient of the graph at the point A.
21. | GCSE Higher |
The graph of y = f(x) is drawn accurately on the grid.
(a) Write down the coordinates of the turning point of the graph.
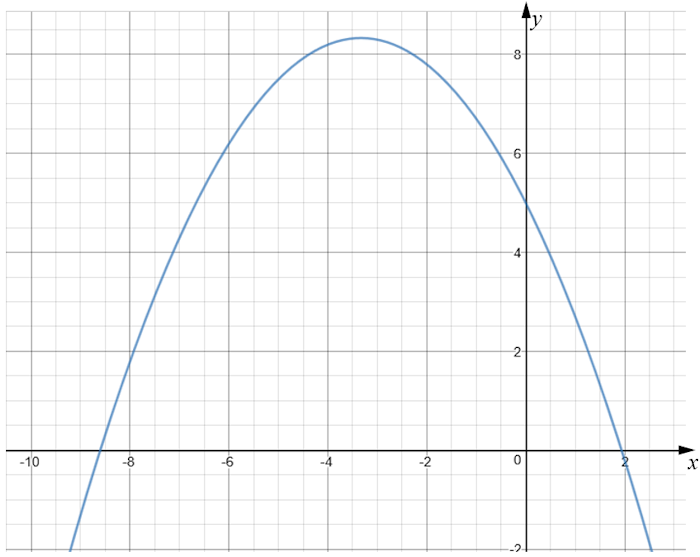
(b) Write down estimates for the roots of f(x) = 0
(c) Use the graph to find an estimate for f(-5.5).
22. | GCSE Higher |
(a) By completing the square, solve \(x^2+8x+13=0\) giving your answer to three significant figures.
(b) From the completed square you found in part (a) find the minimum value of the curve \(y=x^2+8x+13\).
23. | GCSE Higher |
Suppose a rhombus ABCD is drawn on a coordinate plane with the point A situated at (4,7). The diagonal BD lies on the line \(y = 2x - 5 \)
Find the equation the line that passes through A and C.
24. | GCSE Higher |
The graph of the curve with equation y = \(f(x)\) is shown on the grid below.
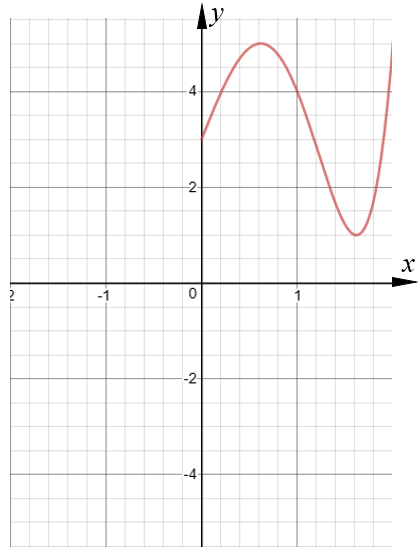
(a) On the grid above, sketch the graph of the curve with equation \(y = f(–x)\)
The red curve with equation \(y = x^2-5x+4\) is transformed by a translation to give the blue curve such that the point (2.5, -2.25) on the red curve is mapped to the point (-2.5, -2.25) on the blue curve.
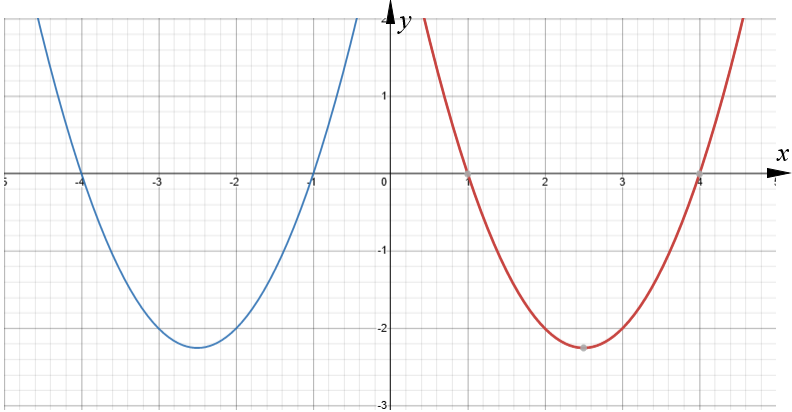
(b) Find an equation for the blue curve.
25. | GCSE Higher |
The graph shows the temperature (\(T\)) of an unidentified flying object over a period of 10 seconds (\(t\)).
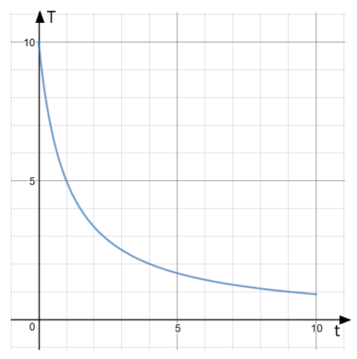
Use the graph to work out an estimate of the rate of decrease of temperature at 7 seconds. You must show your working.
26. | GCSE Higher |
The graph of the following equation is drawn and then reflected in the x-axis
$$y = 2x^2 - 3x + 2$$(a) What is the equation of the reflected curve?
The original curve is reflected in the y-axis.
(b) What is the equation of this second reflected curve?
27. | GCSE Higher |
(a) Sketch the graph of \( y = f(x) \) for values of \( x \) between \(-5\) and \(5\) given that:
$$ f(x) = \frac{1}{x-1} - x $$
(b) Write down the equations of any asymptotes parallel to the \( y \)-axis.
(c) Find the coordinates of the y-axis intercept.
(d) Find the coordinates of the x-axis intercepts.
(e) Find a value of \( k \) for which \( g(x) = kx \) does not intercept \( f(x)\).
(f) Draw the graph of \(h(x)=x-3\) on the same set of axes.
(g) Solve the equation \( f(x) = h(x) \).
(h) Find the solutions to the inequality \( f(x) > h(x) \).
28. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram below is a sketch of a curve, a parabola, which is not drawn to scale.
The quadratic graph intersects the x-axis at (-5, 0) and at another point.
It also intersects the y-axis at (0, –10).
Work out the coordinates of the turning point of the graph if its equation is in the form \(y = x^2 + bx + c \).
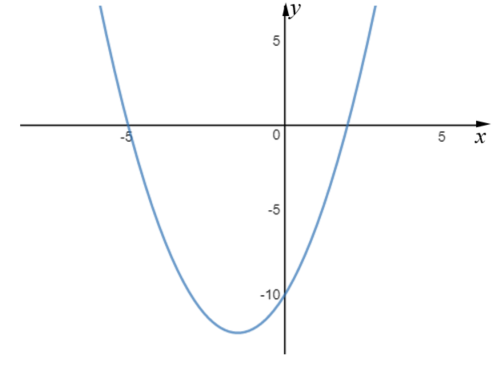
29. | GCSE Higher |
The graph shows the distance travelled, in metres, of a commuter train as it pulls out of a station.
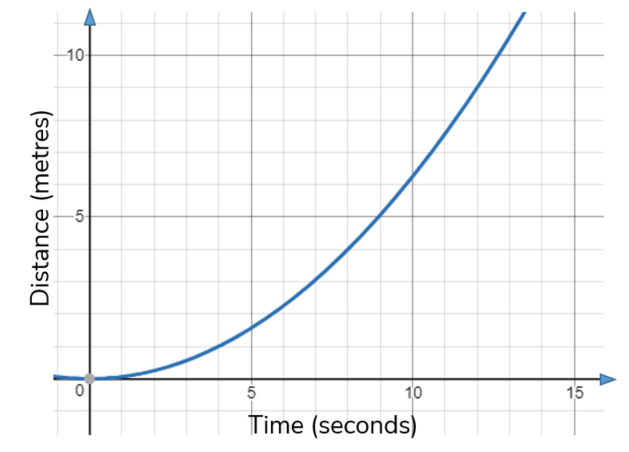
Estimate the speed of the train, in m/s, after 10 seconds. You must show your working.
30. | GCSE Higher |
(a) Find the interval for which \(x^2 - 9x + 18 \le 0\)
(b) The point (-4, -4) is the turning point of the graph of \(y = x^2 + ax + b\), where a and b are integers. Find the values of a and b.
31. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram shows the graph of \( y = f(x) \) for \( -2.1 \leq x \leq 2 \). The y axis is vertical and the x axis is horizontal.
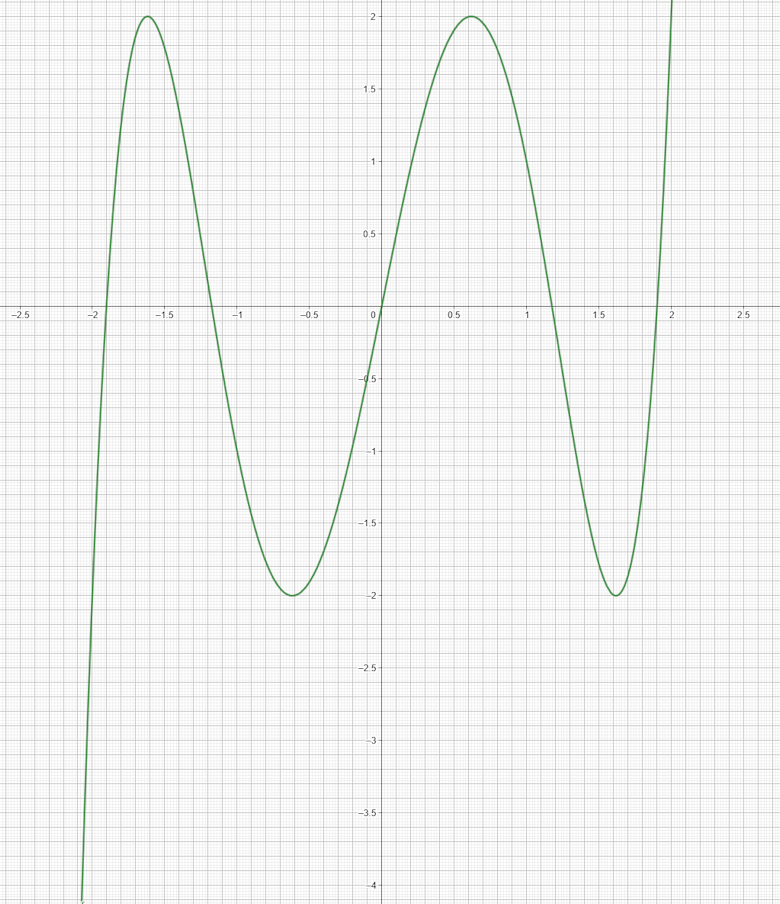
(a) Find \( f(1.2) \).
(b) Solve the equation \( f(x) = 0 \) for \( -2.1 \leq x \leq 2 \).
(c) \( f(x) = k \) has five solutions for \( -2.1 \leq x \leq 2 \) where \( k \) is an integer.
Find the smallest possible value of \( k \).
(d) On the grid, draw a line \( y = mx + x\) so that \( f(x) = mx + c\) has exactly one solution for \( -2.1 \leq x \leq 2 \).
32. | GCSE Higher |
(a) Write \(2x^2+8x+27\) in the form \(a(x+b)^2+c\) where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are integers, by 'completing the square'
(b) Hence, or otherwise, find the line of symmetry of the graph of \(y = 2x^2+8x+27\)
(c) Hence, or otherwise, find the turning point of the graph of \(y = 2x^2+8x+27\)
33. | GCSE Higher |
On the grid below, draw the graph of \(y = 1 - 2x\) for values of \(x\) from -2 to 2.

34. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
Consider the points A(-5, 15). B(4, 6) and C(-8, 12). The line \(L\) passes through the point A and is perpendicular to [BC].
(a) Find the equation of \(L\).
The line \(L\) passes through the point (\(k\), 5).
(b) Find the value of \(k\).
35. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
Consider the following function for \(-2 \le x \le 2\).
$$ f(x) = 5\pi^{-x^4}-1$$(a) Find the values of \(x\) which \( f(x) = 0\).
(b) Sketch the graph of \(\) for \(-2 \le x \le 2\).
36. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
The function \(f\) is defined by:
$$f(x) = \frac{4x+2}{x+1}, \quad \text{ where } x \in \mathbb{R}, x \neq -1 $$(a) Write down the equation of the vertical asymptote of the graph of \(f\).
(b) Write down the equation of the horizontal asymptote of the graph of \(f\).
(c) Find the coordinates of the \(x\)-axis and \(y\)-axis intercepts.
(d) Sketch the graph of \(f\).
37. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
A function \(f\) is defined by \(f(x) = 2 + \dfrac{1}{3-x}, \text{ where } x \in \mathbb{R}, x \neq 3.\)
The graph of \(y=f(x)\) has a vertical asymptote and a horizontal asymptote.
(a) Write down the equation of the horizontal asymptote;
(b) Write down the equation of the vertical asymptote;
Find the coordinates of the point where the graph of \(y\) intersects:
(c) the y-axis;
(d) the x-axis.
38. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
The function \(f\) is defined by \(f(x) = \cos{ax} \) , where \(a > 0\). The following diagram shows part of the graph of \(f\), where x is in radians. There are local maxima at \(x = b , 2b \text{ and } 3b\).
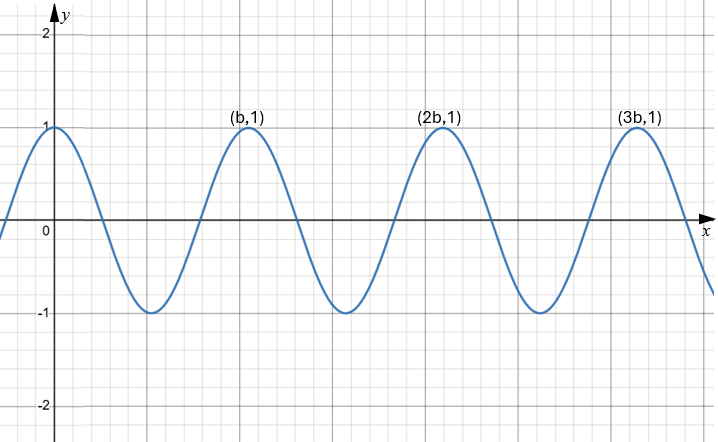
(a) Find an expression for \(b\) in terms of \(a\).
The function \(g\) is defined by \(g(x) = 2\cos{ \dfrac{bx}{3}} \)
(b) On the axes above, sketch the graph of \(g\).
39. | IB Standard |
A function is defined as \(f(x) = 2{(x - 3)^2} - 5\) .
(a) Show that \(f(x) = 2{x^2} - 12x + 13\).
(b) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry of this graph.
(c) Find the coordinates of the vertex of the graph of \(f(x)\).
(d) Write down the y-intercept.
(e) Make a sketch the graph of \(f(x)\).
Let \(g(x) = {x^2}\). The graph of \(f(x)\) may be obtained from the graph of \(g(x)\) by the two transformations:
(f) Find the values of \(j\), \(k\) and \(s\).
40. | IB Studies |
Consider a straight line graph L1, which intersects the x-axis at A(8, 0) and the y-axis at B (0, 4).
(a) Write down the coordinates of C, the midpoint of line segment AB.
(b) Calculate the gradient of the line L1.
The line L2 is parallel to L1 and passes through the point (5 , 9).
(c) Find the equation of L2. Give your answer in the form \(ay + bx + c = 0\) where \(a, b \text{ and } c \in \mathbb{Z}\).
41. | IB Standard |
\(f\) and \(g\) are two functions such that \(g(x)=3f(x+2)+7\).
The graph of \(f\) is mapped to the graph of \(g\) under the following transformations:
A vertical stretch by a factor of \(a\) , followed by a translation \(\begin{pmatrix}b \\c \\ \end{pmatrix}\)
Find the values of
(a) \(a\);
(b) \(b\);
(c) \(c\).
(d) Consider two other functions \(h\) and \(j\). Let \(h(x)=-j(2x)\). The point A(8, 7) on the graph of \(j\) is mapped to the point B on the graph of \(h\). Find the coordinates of B.
42. | IB Standard |
Let \(f(x) = {x^2}\) and \(g(x) = 3{(x+2)^2}\) .
The graph of \(g\) can be obtained from the graph of \(f\) using two transformations.
(a) Give a full description of each of the two transformations.
(b) The graph of \(g\) is translated by the vector \( \begin{pmatrix}-4\\5\\ \end{pmatrix}\) to give the graph of \(h\).
The point \(( 2{\text{, }}-1)\) on the graph of \(f\) is translated to the point \(P\) on the graph of \(h\).
Find the coordinates of \(P\).
43. | IB Standard |
(a) Sketch the graph of \(f(x) = 4\sin x - 5\cos x \), for \(–2\pi \le x \le 2\pi \).
(b) Find the amplitude of \(f\).
(c) Find the the period of \(f\).
(d) Find the \(x\)-intercept that lies between 0 and 3.
(e) Hence write \(f(x)\) in the form \(a \sin (bx + c) \).
(f) Write down one value of \(x\) such that \(f'(x) = 0 \).
(g) Write down the two values of \(p\) for which the equation \(f(x) = p\) has exactly two solutions.
44. | IB Standard |
Let \(f\) and \(g\) be functions such that \(g(x) = 3f(x - 2) + 7\) .
The graph of \(f\) is mapped to the graph of \(g\) under the following transformations: vertical stretch by a factor of \(k\) , followed by a translation \(\left( \begin{array}{l} p\\ q \end{array} \right)\) .
Write down the value of:
(a) \(k\)
(b) \(p\)
(c) \(q\)
(d) Let \(h(x) = - g(2x)\) . The point A(\(8\), \(7\)) on the graph of \(g\) is mapped to the point \({\rm{A}}'\) on the graph of \(h\) . Find \({\rm{A}}'\)
45. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
The graph of \( y = f(|x|) \) for \( -2 \leq x \leq 2 \) is shown in the following diagram.
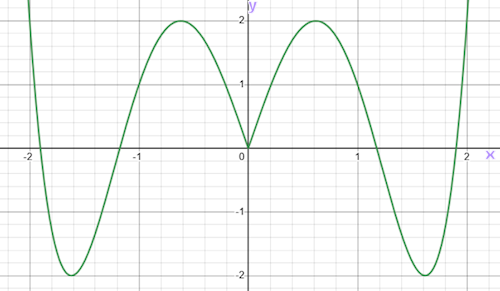
(a) On the following axes, sketch the graph of \( y = |f(|x|)| \) for \( -2 \leq x \leq 2 \).
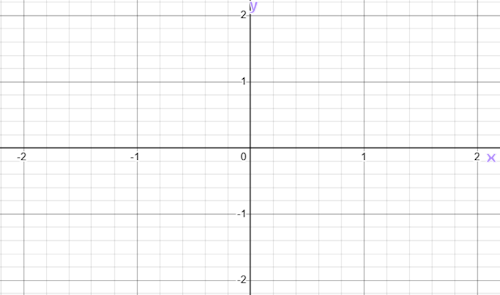
It is given that \( f \) is an odd function.
(b) On the following axes, sketch the graph of \( y = f(x) \) for \( -2 \leq x \leq 2 \).

It is also given that
$$ \int_{0}^{2} f(|x|) \, dx = \dfrac{2}{3} $$(c) Write down the value of
$$ \int_{-2}^{2} f(x) \, dx; $$(d) Evaluate
$$ \int_{-2}^{2} \left( f(|x|) + f(x) \right) \, dx. $$46. | IB Standard |
Let \(f(x) = \frac{9x-3}{bx+9}\) for \(x \neq -\frac9b, b \neq 0\).
(a) The line \(x = 3\) is a vertical asymptote to the graph of \(f\). Find the value of b.
(b) Write down the equation of the horizontal asymptote to the graph of \(f\).
(c) The line \(y = c\) , where \(c\in \mathbb R\) intersects the graph of \( \begin{vmatrix}f(x) \end{vmatrix} \) at exactly one point. Find the possible values of \(c\).
47. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
The following diagram shows the graph of \(f'\), the first derivative of a function \(f\).
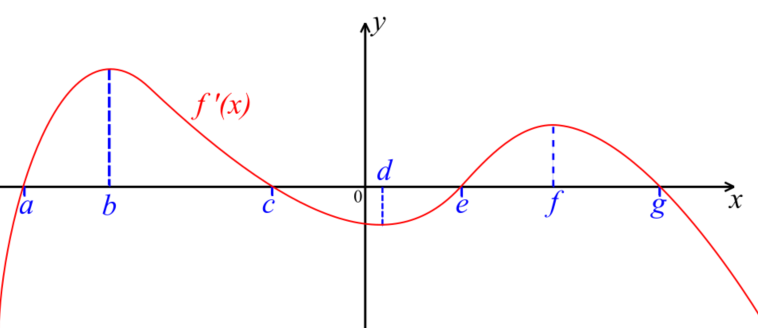
The graph of \(f'\) has x-intercepts at \(x=a, x=c, x=e \text{ and } x=g\). It has local maximum points at \(x=b \text{ and } x=f \) and a local minimum point at \( x=d \).
(a) Find all the values of \(x\) where the graph of \(f\) is increasing. Justify your answer.
(b) Find all the values of \(x\) where the graph of \(f\) has a local maximum. Justify your answer.
(c) Find all the values of \(x\) where the graph of \(f\) has a local minimum. Justify your answer.
(d) Find all the values of \(x\) where the graph of \(f\) has points of inflection and determine which of these is a horizontal point of inflection.
(e) The total area of the region enclosed by graph of \(f'\) and the x-axis for \(a \lt x \lt e\) is 6.
Given that \( f(a) + f(e) = 3 \), find the value of \(f(c)\).
48. | IB Standard |
Two functions are defined as follows: \(f(x) = 2\ln x\) and \(g(x) = \ln \frac{x^2}{3}\).
(a) Express \(g(x)\) in the form \(f(x) - \ln a\) , where \(a \in {{\mathbb{Z}}^ + }\) .
(b) The graph of \(g(x)\) is a transformation of the graph of \(f(x)\) . Give a full geometric description of this transformation.
If you would like space on the right of the question to write out the solution try this Thinning Feature. It will collapse the text into the left half of your screen but large diagrams will remain unchanged.
The exam-style questions appearing on this site are based on those set in previous examinations (or sample assessment papers for future examinations) by the major examination boards. The wording, diagrams and figures used in these questions have been changed from the originals so that students can have fresh, relevant problem solving practice even if they have previously worked through the related exam paper.
The solutions to the questions on this website are only available to those who have a Transum Subscription.
Exam-Style Questions Main Page
To search the entire Transum website use the search box in the grey area below.