
 |
Exam-Style Questions on AnglesProblems on Angles adapted from questions set in previous Mathematics exams. |
1. | GCSE Higher |
The exterior angle of a regular polygon is 72°
What is the name of the regular polygon?
2. | GCSE Higher |
Find the number of sides of a regular polygon with interior angle 140°
3. | GCSE Higher |
The points B, C, D, E and F are on a circle. DAE and CAB are straight lines and AB= BE.
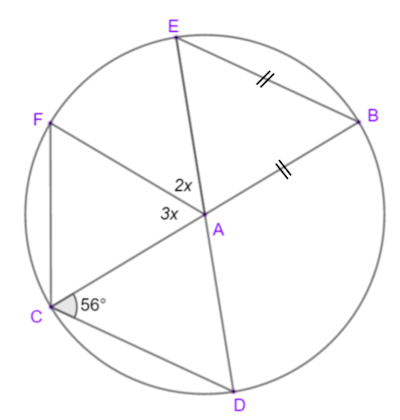
Calculate the value of \(x\).
4. | GCSE Higher |
The points B, C, D and E lie on the circle with centre at A.
FBE is a straight line.
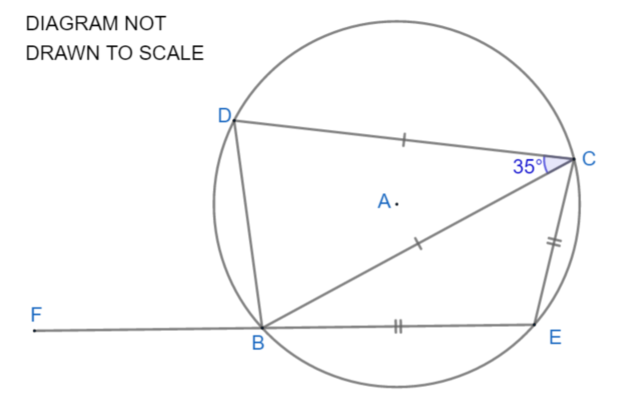
DC = BC
BE = EC
Angle DCB is 35°
Find angle DBF.
You must give a reason for each stage of your working.
5. | GCSE Higher |
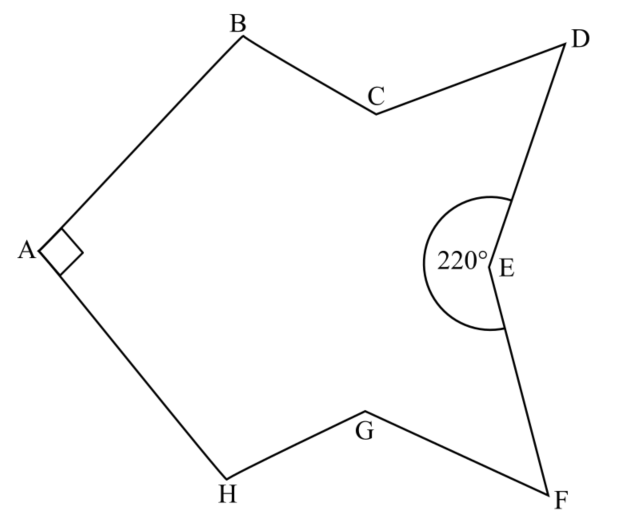
The diagram, not drawn to scale, show a polygon with one line of symmetry, AE.
Angle HAB is 90° and interior angle DEF is 220°.
Work out the size of angle ABC which is half the size of interior angle BCD and twice the size of angle CDE.
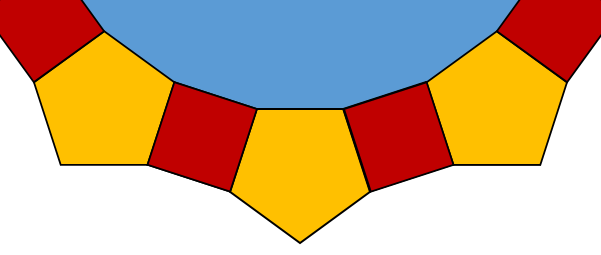
6. | GCSE Higher |
A number of regular pentagons and squares are arranged around the outside of a large blue regular polygon. Just the lower part of the arrangement is shown below.
How many sides does the large blue regular polygon have?
7. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram below shows two parallel lines, AB and CD, crossed by a transversal line EF. Find the values of \(w\), \(x\) and \(y\).
.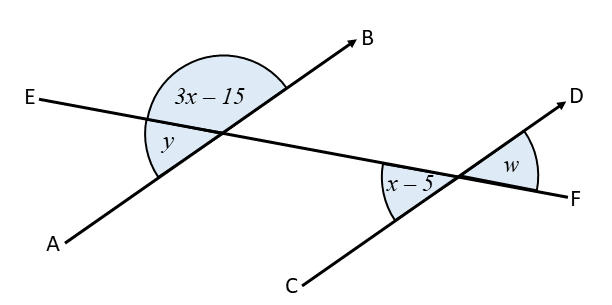
All angles are in degrees.
8. | GCSE Higher |
In the following diagram AD is parallel to CE and AD = CD. Angle AFD is a right angle.
The diagram is not drawn to scale.
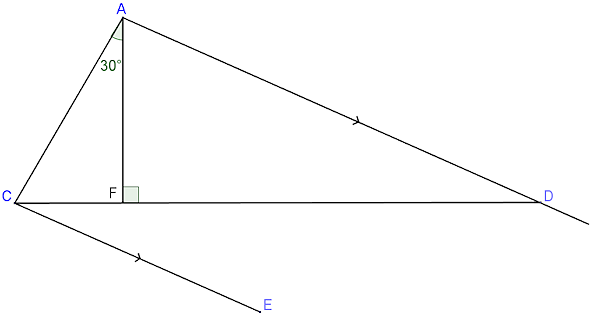
Calculate the size of angle DCE.
9. | GCSE Higher |
B, C, D and E are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O.
BD is a diameter of the circle and the diagram is not drawn to scale.
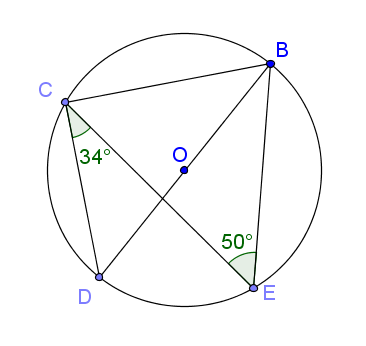
(a) Find the size of angle DBE and give a reason for your answer.
(b) Find the size of angle DBC and give a reason for your answer.
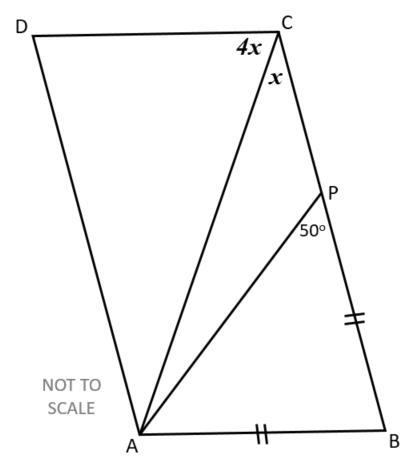
10. | GCSE Higher |
A point P is marked on side BC of parallelogram ABCD such that AB = BP.
Find the value of angle \(x\).
11. | IGCSE Extended |
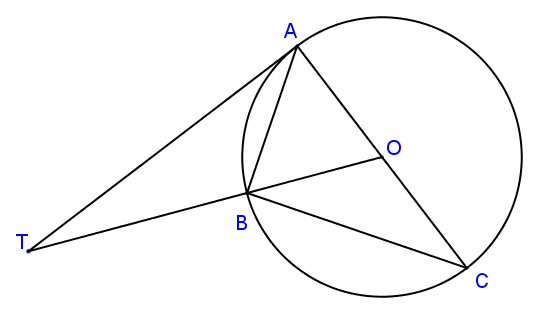
In the diagram above, not drawn to scale, A, B and C are points on a circle, centre O. TA is a tangent to the circle at A and OBT is a straight line. AC is a diameter and angle OTA = 28°.
Calculate
(a) angle AOT
(b) angle ACB
(c) angle ABT
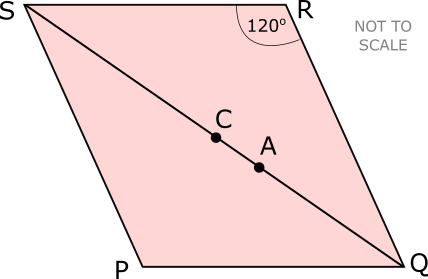
12. | GCSE Higher |
PQRS is a rhombus and C is the midpoint of QS.
The angle QRS is 120o and A is the point on QS such that PA = AQ.
Calculate the size of angle CPA.
13. | IGCSE Extended |
The diagrams are not drawn to scale
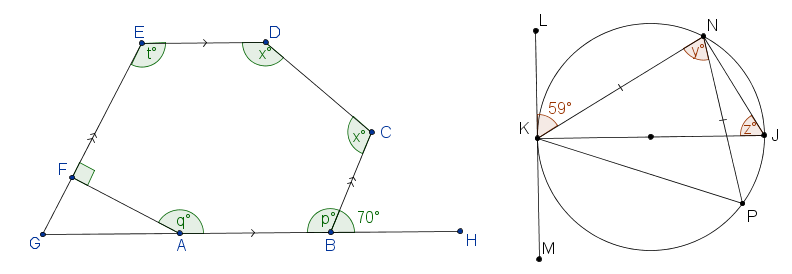
|
ABCDEF is a hexagon with AB parallel to ED and BC parallel to FE. GFE and GABH are straight lines. Angle CBH = 70o and angle EFA = 90o. Calculate the values of: (a) \(p\); (b) \(q\); (c) \(t\); (d) \(x\). |
K, P, J and N are points on a circle and KN = NP. KJ is a diameter and LKM is the tangent to the circle at K. Angle LKN = 59o. Find the values of: (e) \(y\); (f) \(z\). |
If you would like space on the right of the question to write out the solution try this Thinning Feature. It will collapse the text into the left half of your screen but large diagrams will remain unchanged.
The exam-style questions appearing on this site are based on those set in previous examinations (or sample assessment papers for future examinations) by the major examination boards. The wording, diagrams and figures used in these questions have been changed from the originals so that students can have fresh, relevant problem solving practice even if they have previously worked through the related exam paper.
The solutions to the questions on this website are only available to those who have a Transum Subscription.
Exam-Style Questions Main Page
To search the entire Transum website use the search box in the grey area below.