
 |
Exam-Style Questions.Problems adapted from questions set for previous Mathematics exams. |
1. | IB Standard |
The graph of \(f(x)=8-x^2\) crosses the x-axis at the points A and B.
(a) Find the x-coordinate of A and of B.
(b) The region enclosed by the graph of \(f\) and the x-axis is revolved 360o about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
2. | IB Standard |
The acceleration, \(a\) ms-2 , of an object at time \(t\) seconds is given by
$$a=\frac1t+4sin3t, (t\ge1)$$The object is at rest when \(t=1\).
Find the velocity of the object when \(t=7\).
3. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
Find:
$$ \int^{16}_9 \frac{6-2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}} dx $$by first writing the algebraic fraction in the form \(ax^b+c\).
4. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
The diagram below shows part of the graph of \(y = \dfrac{2x}{9-x^2}\)
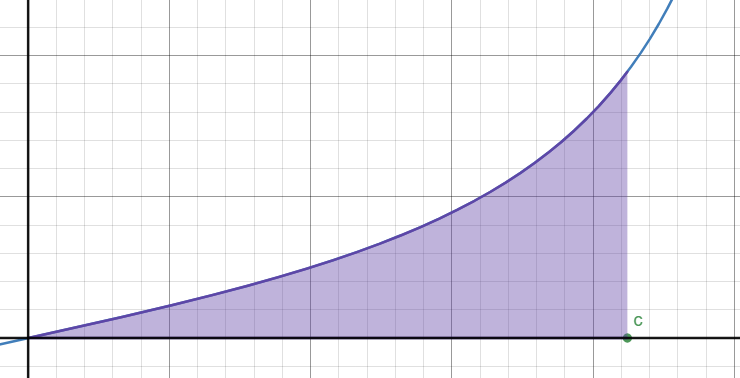
The shaded region is bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line \(x = c\)
The area of this region is \(\ln{2}\)
Find the value of \(c\).
5. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
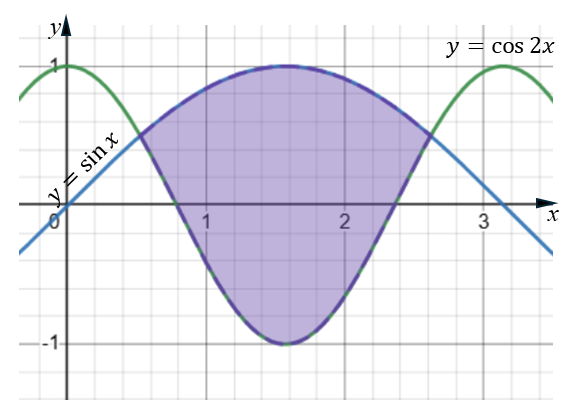
Consider the region where \(0 \lt x \lt \pi \) and \(\sin{x} \gt \cos{2x} \)
Find the area enclosed by the graphs of \(y=\sin{x} \) and \(y= \cos{2x} \)
6. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
The function \(f\) is defined by \(f(x) = 8 - 5 \sin{x} \), for \( x \ge 0 \).
The diagram shows part of the graph of \(y = f (x) \).
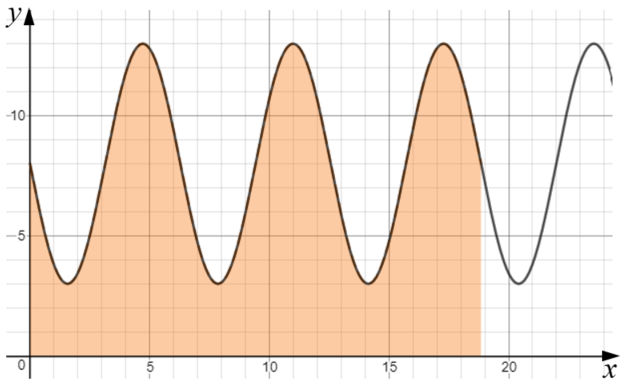
The shaded region is enclosed by the graph of \(y=f(x)\) and the x-axis for the first three periods of the function.
(a) Find the exact value of the x-coordinate of the right side of the shaded region.
(b) Show that the area of the shaded region is \( 48 \pi \).
A hemisphere has a total surface area in square centimetres equal to the shaded area in the previous diagram.
(c) Find the radius of the hemisphere.
7. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
A particle moves in a straight line such that its velocity, \(v\) ms-1, at time \(t\) seconds is given by:
$$ v(t)=10e^{-\frac{t}{7}} \sin\left(\frac{t}{2}\right) $$for \( 0 \le t \le 4 \pi\). The graph of \(v\) is shown in the following diagram.

Let \(t_1 \) be the first time when the particle's acceleration is zero.
(a) Find the value of \(t_1\).
(b) Find the distance travelled by the particle between \(t = t_1 \), and t = \(4 \pi \).8. | A-Level |
(a) Use the trapezium rule with 4 ordinates to estimate to 2 decimal places the value of
$$ \int^{\frac{2\pi}{3}}_0 \sin{x} \; \text{dx} $$(b) State whether this estimate is an overestimate or underestimate of the area.
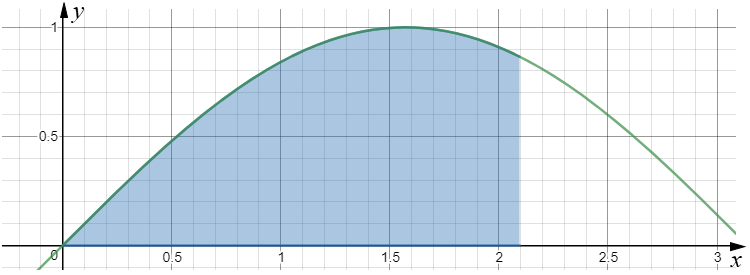
[Note: If knowing about radians is not part of your course then \( \frac{2\pi}{3} \) can be replaced with 120°.]
9. | IB Standard |
Consider the graph of the function \(f(x)=x^2+2\).
(a) Find the area between the graph of \(f\) and the x-axis for \(2\le x \le 3\).
(b) If the area described above is rotated 360o around the x-axis find the volume of the solid formed.
10. | A-Level |
(a) Express the algebraic fraction
$$ \frac{6x^2 - 47x + 49}{(5-x)(1-2x)} $$in the form
$$A + \frac{B}{5-x} + \frac{C}{1-2x} $$where \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) are integers.
(b) Hence show that the following integral equates to 3.03 correct to three significant figures.
$$ \int^{0.25}_0 \frac{6x^2 - 47x + 49}{(5-x)(1-2x)} dx $$11. | IB Standard |
Make a sketch of a graph showing the velocity (in \(ms^{-1}\)) against time of a particle travelling for six seconds according to the equation:
$$v=e^{\sin t}-1$$(a) Find the point at which the graph crosses the \(t\) axis.
(b) How far does the particle travel during these first six seconds?
12. | IB Standard |
Find the value of \(a\) if \(\pi \lt a \lt 2\pi\) and:
$$ \int_\pi^a sin3x dx = -\frac13$$13. | IB Standard |
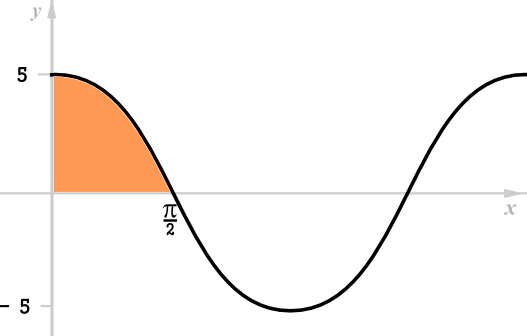
This graph represents the function \(f:x\to a \cos x, a\in \mathbf N\)
(a) Find the value of \(a\).
(b) Find the area of the shaded region.
14. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
Consider the function \(f\) defined by \(f(x) = 25e^{x-5}\) for \(x \in \mathbb{R}^+\).
(a) Find the coordinates of the points where the graph of \(f\) intersects the line \(y=x\).
The line \(L\) has a gradient of \(-1\) and is a normal to the graph of \(f\) at the point \(R\).
(b) Find the exact coordinates of \(R\).
(c) Show that the equation of the line \(L\) is \(y=-x+6- \ln{25}\).
(d) Find the area of the region enclosed by the graph of \(f\) and its inverse.
15. | IB Standard |
The following diagram shows the graph of \(f(x) = \cos(e^x) \; \text{for} \; 0 \le x \le 0.5\).
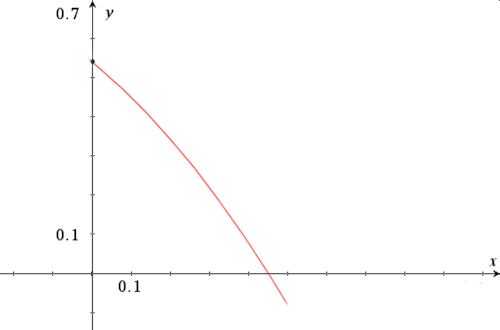
(a) Find the x-intercept of the graph of \(f(x)\).
The region enclosed by the graph of \(f(x)\), the y-axis and the x-axis is rotated 360° about the x-axis.
(b) Find the volume of the solid formed.
16. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
Let \(f(x) = \frac{ln3x}{kx} \) where \( x \gt 0\) and \( k \in \mathbf Q^+ \).
(a) Find an expression for the first derivative \(f'(x) \).
The graph of \(f\) has exactly one maximum point at P.
(b) Find the x-coordinate of P.
The graph of \(f\) has exactly one point of inflection at Q.
(c) Find the x-coordinate of Q.
(d) The region enclosed by the graph of \(f\), the x-axis, and the vertical lines through P and Q has an area of one square unit, find the value of \(k\).
If you would like space on the right of the question to write out the solution try this Thinning Feature. It will collapse the text into the left half of your screen but large diagrams will remain unchanged.
The exam-style questions appearing on this site are based on those set in previous examinations (or sample assessment papers for future examinations) by the major examination boards. The wording, diagrams and figures used in these questions have been changed from the originals so that students can have fresh, relevant problem solving practice even if they have previously worked through the related exam paper.
The solutions to the questions on this website are only available to those who have a Transum Subscription.
Exam-Style Questions Main Page
To search the entire Transum website use the search box in the grey area below.