
 |
Exam-Style Questions.Problems adapted from questions set for previous Mathematics exams. |
1. | GCSE Higher |
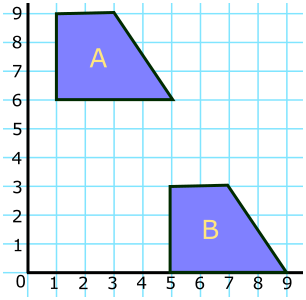
(a) Shape \(A\) is translated to shape \(B\) using the vector \( \begin{pmatrix}m\\n\\ \end{pmatrix}\). What are the values of \(m\) and \(n\)?
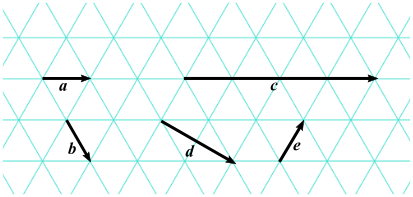
(b) Vectors \(a, b, c, d\) and \(e\) are drawn on an isometric grid. Write each of the vectors \(c, d\) and \(e\) in terms of \(a\) and/or \(b\).
2. | IB Standard |
Consider two perpendicular vectors \(p\) and \(q\).
(a) Let \(r=p-q\). Draw a diagram to show what this relationship might look like.
(b) If \(p=\begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ 1 \\ -3 \\ \end{pmatrix}\) and \(q=\begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ n \\ -5 \\ \end{pmatrix}\), where \(n\in \mathbb Z\), find \(n\).
3. | IB Standard |
George and Hugo like to fly model airplanes. On one day George's plane takes off from level ground and shortly after that Hugo's plane takes off.
The position of George’s plane \(s\) seconds after it takes off is given by \(\begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 0 \\ \end{pmatrix} + s\begin{pmatrix} 5 \\ -2 \\ 6 \\ \end{pmatrix} \) where the distances are in metres.
(a) Find the speed of George’s plane to the nearest integer.
(b) Find the height of George’s plane after four seconds.
The position of Hugo’s airplane \(t\) seconds after it takes off is given by \(\begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ -4 \\ 0 \\ \end{pmatrix}+t\begin{pmatrix} 7 \\ -2 \\ 9 \\ \end{pmatrix} \) where the distances are in metres.
(c) Show that the paths of the planes are not perpendicular.
The two airplanes collide at the point \((46, -16, 54)\).
(d) How long after George’s plane takes off does Hugo’s plane take off ?
4. | IB Standard |
The line \(L_1\) passes through the points A(3, 5, 1) and B(3, 6, 0).
(a) Show that \(AB=\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 1 \\ -1 \\ \end{pmatrix}\)
(b) Find a direction vector for \(L_1\)
(c) a vector equation for \(L_1\)
Another line \(L_2\) has equation \(\begin{pmatrix} 8 \\ 3 \\ -2 \\ \end{pmatrix} + t \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \\ \end{pmatrix}\). The lines \(L_1\) and \(L_2\) intersect at the point P.
(d) Find the coordinates of P.
(e) Find a direction vector for \(L_2\).
(f) Hence, find the angle between \(L_1\) and \(L_2\).
5. | IB Standard |
Two points \(A\) and \(B\) have coordinates (1 , 3 , 6) and (8 , 7 , 10) respectively.
(a) Find \( \overrightarrow{AB} \) in terms of the unit vectors \(i, j\) and \(k\).
(b) Find \(\mid\overrightarrow{AB} \mid\)
Let \( \overrightarrow{AC} = 5i + 2j - k\)
(c) Find the angle between \(AB\) and \(AC\).
(d) Find the area of triangle \(ABC\).
(e) Hence or otherwise find the shortest distance from \(C\) to the line through \(A\) and \(B\).
6. | A-Level |
The points A and B have coordinates \((3,-2,1)\) and \((4, 0, -1)\) respectively.
The line \(l\) has the following equation:
$$ r= \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 2 \\ 0 \\ \end{pmatrix} + \lambda \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ -2 \\ 0 \\ \end{pmatrix} $$The point C lies on \(l\) where \(\lambda = 3\).
(a) Find the coordinates of C.
(b) Find the acute angle ABC, giving your answer to the nearest tenth of a degree.
(c) The point D lies on a line through A and B such that angle ADC is a right angle. Find the coordinates of D.
(d) The point E completes the parallelogram ACBE. Find the coordinates of E.
7. | IB Analysis and Approaches |
Consider the vectors \(\mathbf{a}\) and \(\mathbf{b}\) such that \(\mathbf{a} = \begin{pmatrix} 16 \\ -12 \end{pmatrix} \) and \( |\mathbf{b}| = 11\).
(a) Find the possible range of values for \(|\mathbf{a+b}|\).
Consider the vector \(\mathbf{p}\) such that \(\mathbf{p=a+b}\).
(b) Given that \(|\mathbf{a+b}|\) is a minimum, find \(\mathbf{p}\).
Consider the vector q such that \(\mathbf{q} = \begin{pmatrix}x \\ y \end{pmatrix} \) , where \(x,y \in \mathbb{R} \).
(c) Find \(\mathbf{q}\) such that \(\mathbf{|q| = |b|}\) and \(\mathbf{q}\) is perpendicular to \(\mathbf{a}\).
If you would like space on the right of the question to write out the solution try this Thinning Feature. It will collapse the text into the left half of your screen but large diagrams will remain unchanged.
The exam-style questions appearing on this site are based on those set in previous examinations (or sample assessment papers for future examinations) by the major examination boards. The wording, diagrams and figures used in these questions have been changed from the originals so that students can have fresh, relevant problem solving practice even if they have previously worked through the related exam paper.
The solutions to the questions on this website are only available to those who have a Transum Subscription.
Exam-Style Questions Main Page
To search the entire Transum website use the search box in the grey area below.