
 |
Exam-Style Questions.Problems adapted from questions set for previous Mathematics exams. |
1. | GCSE Higher |
Find \(4a - b\) as a column vector.
2. | GCSE Higher |
Calculate the vector \(3a - 2b\) if the vectors \(a\) and \(b\) are:
$$ a = \begin{pmatrix} -2 \\ -5 \\ \end{pmatrix} $$ $$ b = \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ -3 \\ \end{pmatrix} $$3. | GCSE Higher |
$$u=\begin{pmatrix}3\\-2\end{pmatrix}\quad v=\begin{pmatrix}9\\-12\end{pmatrix}$$
(a) Find \(u+v\).
(b) Find \(u-3v\).
(c) Find \(|v|\).
4. | GCSE Higher |
The diagram shows triangle \(ABC\) and a line joining two of its sides.

In the diagram \( \overrightarrow{CA} = a \) and \( \overrightarrow{CB} = b \). \( \quad \quad CT : TA = 1 : 2 \) and \( AM : AB = 1 : 2 \).
Find, in terms of \( a \) and \( b \), in its simplest form:
(a) \( \overrightarrow{MB} \)
(b) \( \overrightarrow{TM} \).
(c) \( MT \) is extended to the point \( Z \). $$ \overrightarrow{MZ} = -\tfrac{1}{2}(a+3b) $$ Show that \( Z \) lies on \( BC \) extended.
5. | IGCSE Extended |
OABC is a parallelogram with O as origin. The position vector of A is \(a\) and the position vector of C is \(c\).
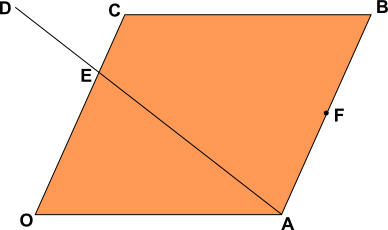
F is the mid-point of AB and the point E divides the line OC such that OE:EC = 2:1.
The point E also divides the line AD such that AE:ED = 3:2.
Find the following in terms of \(a\) and \(c\).
(a) \(\overrightarrow{OB}\)
(b) \(\overrightarrow{AC}\)
(c) \(\overrightarrow{AE}\)
(d) the position vector of F.
(e) \(\overrightarrow{AD}\)
(f) \(\overrightarrow{BD}\)
6. | GCSE Higher |
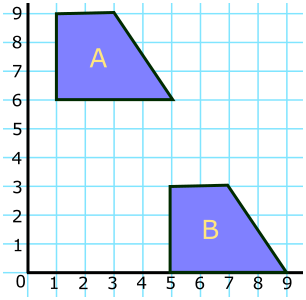
(a) Shape \(A\) is translated to shape \(B\) using the vector \( \begin{pmatrix}m\\n\\ \end{pmatrix}\). What are the values of \(m\) and \(n\)?
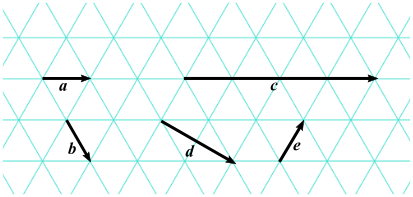
(b) Vectors \(a, b, c, d\) and \(e\) are drawn on an isometric grid. Write each of the vectors \(c, d\) and \(e\) in terms of \(a\) and/or \(b\).
7. | GCSE Higher |
ABCD is a quadrilateral. The points E, F, G and H are the midpoints of the sides of this quadrilateral.
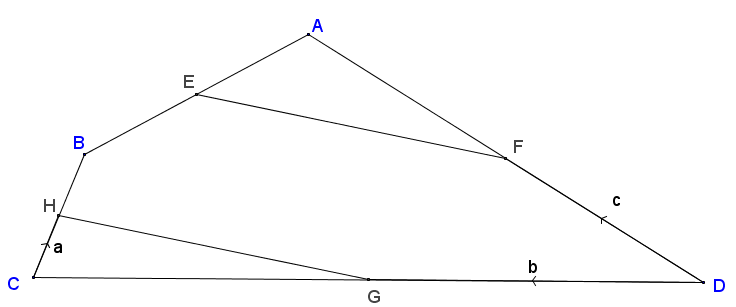 $$\vec{CH} = a, \vec{DG} = b \text{ and } \vec{DF} = c$$
$$\vec{CH} = a, \vec{DG} = b \text{ and } \vec{DF} = c$$
Show that HG is parallel to EF.
8. | IGCSE Extended |
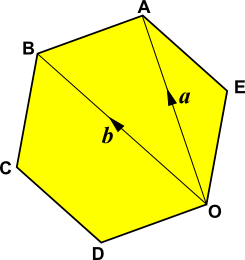
ABCDOE is a regular hexagon with O as origin. The position vector of A is \(a\) and the position vector of B is \(b\).
Find the following in terms of \(a\) and \(b\).
(a) \(\overrightarrow{BA}\)
(b) \(\overrightarrow{OE}\)
(c) the position vector of C.
If the sides of the hexagon are each of length 10cm calculate:
(d) the size of angle \(BCD\).
(e) the area of triangle \(BCD\).
(f) the length of the line from B to D.
(g) the area of the hexagon.
9. | GCSE Higher |
Consider a triangle ABC where M is the midpoint of AB and F is the point on BC where BF:FC = 3:4.
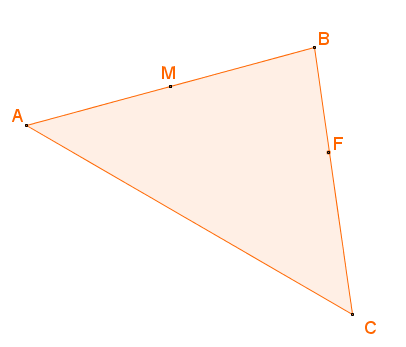
(a) If \(\overrightarrow{AB}=b\) and \(\overrightarrow{AC}=c\) work out \(\overrightarrow{MF}\) in terms of \(b\) and \(c\) giving your answer in its simplest form.
(b) Use your answer to part (a) to explain whether MF is parallel to AC or not.
10. | GCSE Higher |
In the parallelogram OABC two of the sides can be represented by vectors \(a\) and \(c\).
\( \overrightarrow{OA} = a \) and \( \overrightarrow{OC} = c \)
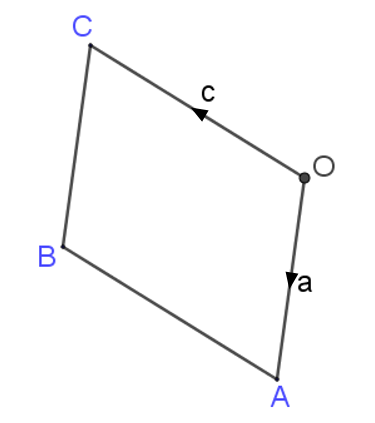
\( X \) is the midpoint of the line \( AC \).
\( OCD \) is a straight line such that \(OC:CD = k:1 \)
Given that \( \overrightarrow{XD} = 3c - \frac12 a \) find the value of \( k \).
11. | GCSE Higher |
ABCD is a quadrilateral
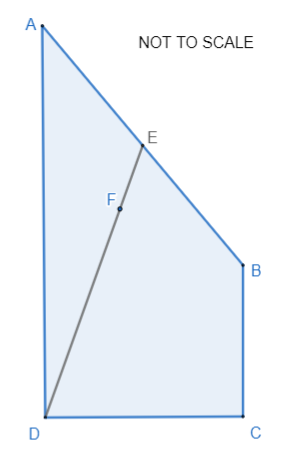
\(\overrightarrow{AB} = p\)
\(\overrightarrow{BC} = q\)
\(\overrightarrow{CD} = 2q - p\)
(a) Express \(\overrightarrow{AD}\) in terms of \(p\) and/or \(q\) giving your answer in its simplest form.
E is the midpoint of AB.
F is the point on DE such that DF : FE = n : 1
AFC is a straight line.
(b) Work out the value of n.
12. | IGCSE Extended |
(a) If A is the point (3,5) write down the position vector of A.
(b) If B is the point (6,9) find \(\mid\overrightarrow{AB} \mid\) the magnitude of \( \overrightarrow{AB}\).
The following diagram is not to scale.

\(O\) is the origin, \(\overrightarrow{OP}=p\) and = \(\overrightarrow{OQ}=q\).
\(OP\) is extended to \(R\) so that \(OP=PR\).
\(OQ\) is extended to \(S\) so that \(OQ=QS\).
(c) Write down \(\overrightarrow{RQ}\) in terms of \(p\) and \(q\).
(d) \(PS\) and \(RQ\) intersect at \(M\) and \(RM=2 MQ\).
Use vectors to find the ratio \(PM:PS\), showing all your working.
13. | GCSE Higher |
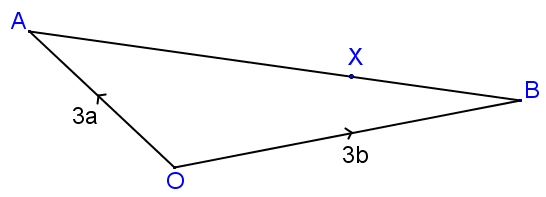
In the diagram above (not drawn to scale) \(X\) is the point on \(AB\) such that \(AX:XB = 9:4\).
The position vector of \(A\) is \(3a\) and the position vector of \(B\) is \(3b\).
Find the value of \(k\) if \(\vec{OX} = k(4a + 9b)\) where \(k\) is a scalar quantity.
14. | IB Standard |
Consider two perpendicular vectors \(p\) and \(q\).
(a) Let \(r=p-q\). Draw a diagram to show what this relationship might look like.
(b) If \(p=\begin{pmatrix} 4 \\ 1 \\ -3 \\ \end{pmatrix}\) and \(q=\begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ n \\ -5 \\ \end{pmatrix}\), where \(n\in \mathbb Z\), find \(n\).
15. | IB Standard |
Two points \(A\) and \(B\) have coordinates (1 , 3 , 6) and (8 , 7 , 10) respectively.
(a) Find \( \overrightarrow{AB} \) in terms of the unit vectors \(i, j\) and \(k\).
(b) Find \(\mid\overrightarrow{AB} \mid\)
Let \( \overrightarrow{AC} = 5i + 2j - k\)
(c) Find the angle between \(AB\) and \(AC\).
(d) Find the area of triangle \(ABC\).
(e) Hence or otherwise find the shortest distance from \(C\) to the line through \(A\) and \(B\).
If you would like space on the right of the question to write out the solution try this Thinning Feature. It will collapse the text into the left half of your screen but large diagrams will remain unchanged.
The exam-style questions appearing on this site are based on those set in previous examinations (or sample assessment papers for future examinations) by the major examination boards. The wording, diagrams and figures used in these questions have been changed from the originals so that students can have fresh, relevant problem solving practice even if they have previously worked through the related exam paper.
The solutions to the questions on this website are only available to those who have a Transum Subscription.
Exam-Style Questions Main Page
To search the entire Transum website use the search box in the grey area below.